3D printing is an exciting and rapidly growing industry that has made it possible for anyone with a desktop printer to create complex and intricate designs at a relatively low cost. However, even experienced 3D printing enthusiasts are bound to make mistakes from time to time, especially when dealing with new materials or techniques. Here are the 6 most common 3D printing mistakes and how to avoid them.
1. Not Using the Right Temperature
One of the most common 3D printing mistakes is not using the correct temperature for your print material. Different materials have different melting points, and if your printer is not set to the right temperature, your prints will not come out as expected. Before starting your print, be sure to check the recommended temperature range for the material you’re using, and make sure your printer is set to the appropriate temperature.
To avoid this mistake, it's important to understand the difference between the printing temperature and the bed temperature. The printing temperature is the temperature at which the filament is melted and extruded, while the bed temperature is the temperature at which the build platform is heated.
The printing temperature should be set according to the manufacturer's recommendations for the specific filament type you're using. Most 3D printing filaments come with a recommended temperature range that you should stick to. If you don't know what the recommended temperature range is, it's best to start with the low end and work your way up.
The bed temperature, on the other hand, is important for ensuring proper adhesion between the printed object ad the build platform. If the bed temperature is too low, the printed object may warp or come loose from the build platform. If the bed temperature is too high, the bottom of the printed object may become distorted.
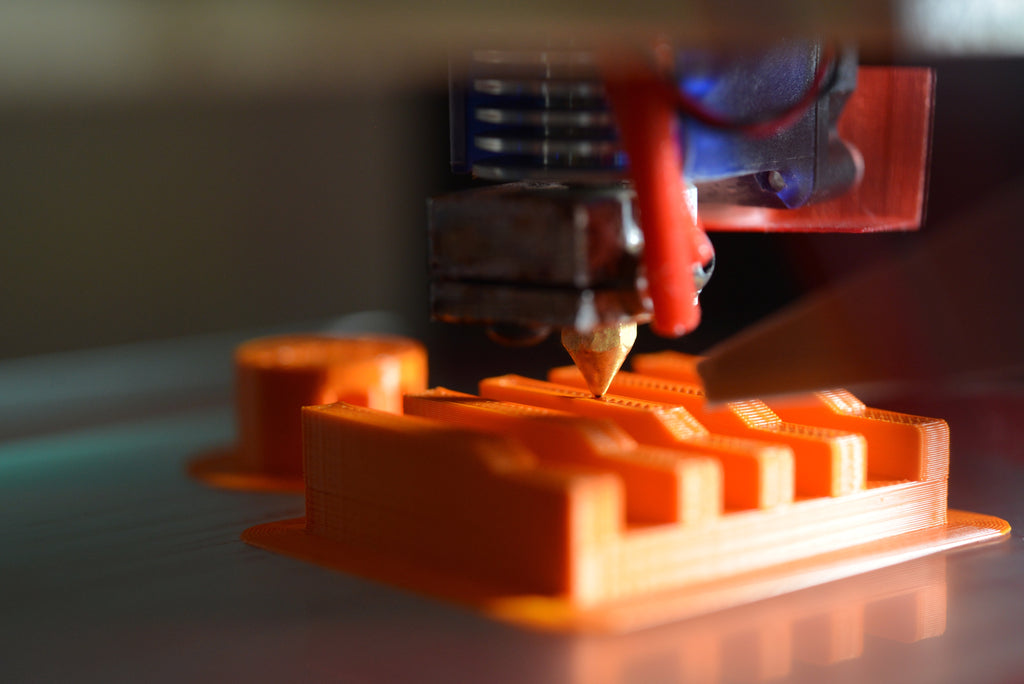
2. Not Using the Right Bed Adhesion
Another common issue is poor bed adhesion. This occurs when the first layer of your print doesn’t stick to the build plate, causing the print to fail. To avoid this, make sure your build plate is clean and level, and use the correct bed adhesion method for your material. Some materials require a heated build plate, while others may require a specific type of adhesive to stick properly.
The first step to ensuring proper bed adhesion is to make sure your build platform is clean and free of debris. Even small particles of dust or dirt can prevent the first layer of your print from sticking properly. Use a lint-free cloth and some isopropyl alcohol to clean the surface of the build platform before each print.
Next, make sure the build platform is level. A level build platform ensures that the distance between the nozzle and the build platform is consistent across the entire surface of the platform, which is critical for ensuring proper bed adhesion.
Lastly, use the correct bed adhesion method for your material. Some materials, like ABS, require a heated build platform to ensure proper adhesion. Others, like PLA, can be printed on a room-temperature build platform. Some materials may require a specific type of adhesive to stick properly, such as a glue stick or painter's tape.
3. Incorrect Retraction Settings
Retraction is the process of pulling the filament back into the nozzle to prevent oozing or stringing between layers. If your retraction settings are incorrect, you may end up with unwanted strings or blobs on your print. To avoid this, adjust your retraction settings to match the material you’re using, and test print a small object to ensure the settings are correct before starting a larger print.
Retraction is an important setting to get right because it can greatly impact the overall quality of your 3D prints. If the retraction is too high, the nozzle may pull too much filament back, causing gaps or under-extrusion in the printed object. If the retraction is too low, the nozzle may not pull enough filament back, resulting in unwanted strings or blobs.

To adjust your retraction settings, start by printing a small test object with your chosen material. Keep the retraction settings at their default values and note any stringing or oozing that occurs. Then, adjust the retraction settings and print the test object again, repeating this process until you find the optimal settings for your material.
Factors that can affect your retraction settings include the material type, the printing speed, and the temperature. For example, some materials require longer retraction distances than others to prevent oozing, while faster printing speeds may require shorter retraction distances.
4. Incorrect Speed Settings
Speed is another crucial factor to consider when 3D printing. If your printer is moving too fast, it can cause poor print quality or even lead to print failure. On the other hand, if your printer is moving too slow, it can greatly increase the printing time, which can be especially problematic for larger prints.
To avoid speed-related issues, it's important to set your printing speed appropriately for your material and object. Generally, slower speeds are recommended for larger and more complex objects, while faster speeds can be used for smaller and simpler objects.
In addition to print speed, it's also important to consider the speed of your printer's cooling fan. The cooling fan helps to cool down the printed material and prevent warping, but if it's moving too fast or too slow, it can cause issues with the print quality. Make sure to adjust the cooling fan speed as needed based on your material and printing settings.
5. Poor Supports
Supports are structures that are added to a 3D print to provide stability for overhanging sections or other complex geometries. Poor supports can lead to a failed print or result in a print with unwanted deformations.
To avoid this, make sure to generate high-quality support structures for your print. Many 3D printing software programs have built-in support generation tools, but you can also use third-party support generation software for more complex prints.
When generating supports, make sure they are well-attached to the object and that they are easy to remove after printing. Supports that are too thin or too sparse can cause the printed object to sag or deform, while supports that are too thick can be difficult to remove and leave behind unwanted marks or blemishes.
6. Insufficient Cooling
Finally, insufficient cooling can cause a range of issues with your 3D prints. When plastic material is extruded from the printer nozzle, it can become soft and pliable. If it cools too quickly, it can become brittle and lead to unwanted deformations or warping.
To avoid this, make sure your printer has adequate cooling capabilities, including a cooling fan and sufficient ventilation. Adjust the cooling fan speed as needed to ensure the printed object is cooling at an appropriate rate.
In addition, make sure to position your printer in a well-ventilated area to prevent the buildup of fumes and to help with the cooling process. If you are printing with materials that are known to emit fumes, consider using a specialized air filtration system to remove these fumes from the air.
3D printing is an exciting technology that offers a wide range of possibilities for creating unique and complex objects. However, even experienced 3D printing enthusiasts can make mistakes from time to time. By avoiding these common mistakes, you can increase the likelihood of a successful print and create high-quality objects every time. Remember to use the right temperature, bed adhesion, retraction and speed settings, generate high-quality supports, and ensure sufficient cooling for your prints. With a bit of practice and experimentation, you can become a 3D printing expert in no time. Happy printing!

